First Class Tips About How To Set Up A Circuit On Breadboard

How To Build A Simple Circuit On Breadboard Wiring Draw And Schematic
Unlocking the Secrets of Breadboards
1. What's the Big Deal with Breadboards Anyway?
Alright, so you want to build cool electronic gadgets, right? Maybe blink an LED, create a mini-robot, or even build your own musical instrument (think theremin, but less spooky). Well, your first stop on this electrifying journey is the breadboard. Think of it as the LEGO set for electronics — a reusable, solderless way to prototype circuits. No permanent commitment, no burning your fingers with a soldering iron (yet!), just pure creative experimentation.
But don't let its simple appearance fool you. A breadboard is more than just a plastic board with a bunch of holes. It's a meticulously organized system of interconnected metal strips designed to make connecting components a breeze. Understanding how these connections work is key to successfully building and testing your circuits. So, let's dive into the inner workings, shall we?
Imagine a grid. A magical grid where components snap in place and wires connect everything. Thats essentially what a breadboard offers. The holes are strategically placed to accept the leads of resistors, LEDs, integrated circuits (ICs), and all sorts of other electronic goodies. The real magic happens underneath the plastic surface. That's where the metal strips reside, creating the connections that bring your circuit to life.
So, why not just solder everything directly? Well, for one, soldering takes time, skill, and specialized equipment. More importantly, it's permanent. If you make a mistake, you have to desolder (which is even more of a pain!). Breadboards allow you to quickly change connections, test different components, and generally experiment without any irreversible consequences. They are the ultimate playground for circuit tinkerers.

Simple Breadboard Circuit Diagram
Decoding the Breadboard Layout
2. Rows, Columns, and Power Rails
Okay, let's get down to the nitty-gritty (oops, almost slipped there!). The breadboard has a specific layout, and understanding it is crucial for avoiding short circuits and other electronic mishaps. At first glance, it might seem like a random assortment of holes, but theres a method to the madness. Think of it as a tiny electronic city with power grids and residential blocks.
Most breadboards have two sets of power rails running along the sides, typically marked with "+" and "-" symbols (or red and blue lines). These rails provide a convenient way to distribute power throughout your circuit. The "+" rail is usually connected to the positive voltage supply, while the "-" rail is connected to ground (0 volts). Remember to always connect your power supply correctly to avoid damaging your components.
The central area of the breadboard is where the real action happens. This area is divided into two sections, separated by a trough. Each section consists of rows and columns of holes. The holes in each row are connected internally, but the rows themselves are not connected to each other. This means that any components plugged into the same row are electrically connected. The separation in the middle allows you to conveniently mount ICs, which typically have pins on both sides.
So, when you're building your circuit, think about how the components are connected. Use the rows to connect components together, and use the power rails to supply power to the circuit. Remember to keep your wiring neat and organized, and always double-check your connections before applying power. A little bit of planning can save you a lot of frustration later on.

Setting Up Your First Circuit
3. A Step-by-Step Guide to Illuminating Your Imagination
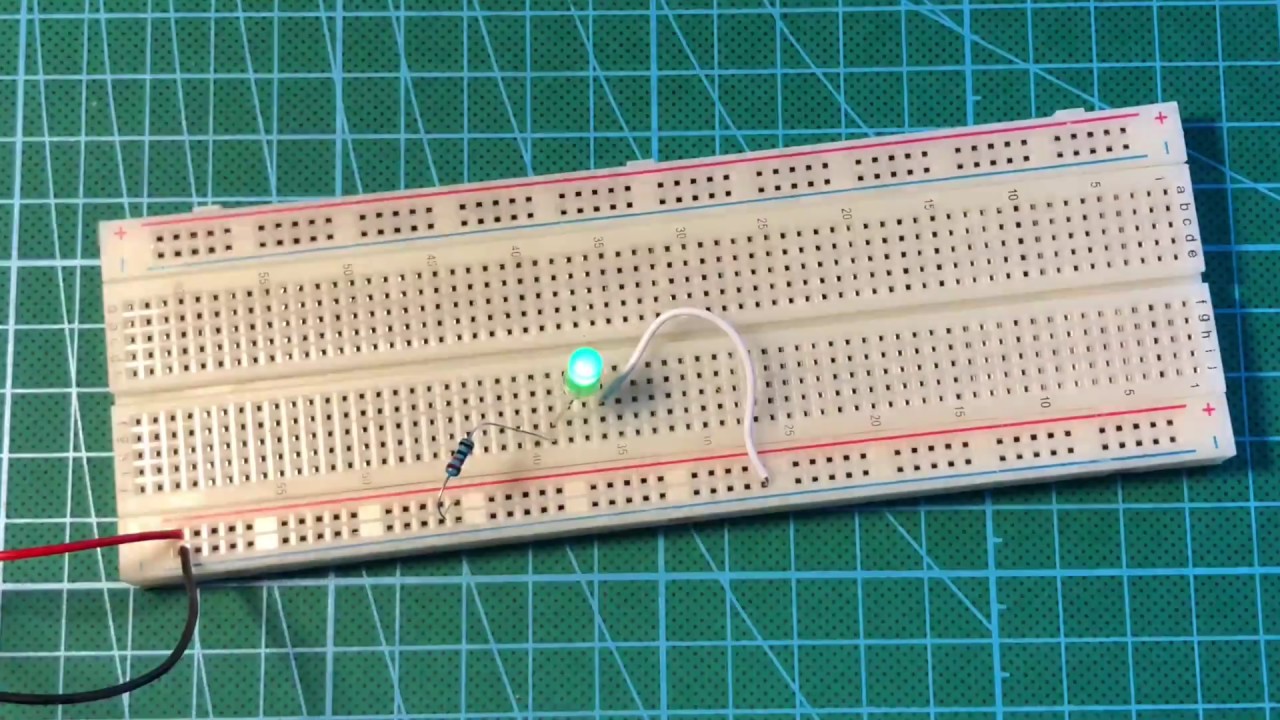
Alright, enough theory! Let's get our hands dirty and build a simple circuit: an LED that blinks. This is the "Hello, World!" of electronics, a fundamental project that teaches you the basics of connecting components on a breadboard. Don't worry, it's easier than it sounds. We'll walk through each step together, and soon you'll be blinking LEDs like a pro.
First, gather your materials. You'll need a breadboard (of course!), an LED (any color will do), a resistor (typically between 220 ohms and 1 kilohm — the color code will tell you the resistance), a power supply (a 5V power supply or a 9V battery with a battery clip will work), and some jumper wires (these are pre-cut wires with solid ends that are perfect for plugging into the breadboard).
Now, let's build the circuit. First, plug the LED into the breadboard. The LED has two leads: a longer lead (the anode, or positive side) and a shorter lead (the cathode, or negative side). Insert the longer lead into one row and the shorter lead into a different row. Next, connect the resistor to the longer lead of the LED. Plug one end of the resistor into the same row as the longer LED lead, and plug the other end of the resistor into a different row. Finally, connect a jumper wire from the free end of the resistor to the positive power rail on the breadboard. Connect another jumper wire from the shorter lead of the LED to the negative power rail (ground).
Once you've connected everything, it's time to apply power. Connect your power supply to the power rails on the breadboard. If everything is connected correctly, the LED should light up. If it doesn't, double-check your connections and make sure the LED is not backwards. If the LED still doesn't light up, try using a different resistor or a different LED. Once you get the LED to light up, you've successfully built your first circuit! Congratulations! To make it blink, we'd need more components (like a 555 timer IC), but thats a story for another day!
Beyond the Basics
4. Harnessing the Power of Organization and Good Practices
So, you've conquered the blinking LED. What's next? Well, the breadboard universe is vast and full of possibilities. But before you dive into more complex circuits, let's talk about some tips and tricks that will help you become a true breadboard master. These practices will save you time, reduce frustration, and ultimately make your projects more successful.
First, organization is key. Keep your components and wires neatly organized. Use different colored wires to distinguish between power, ground, and signal lines. Label your wires if necessary. A cluttered breadboard is a recipe for disaster. Trust me, you'll thank yourself later when you're trying to debug a complex circuit and you can easily trace the connections.
Second, use the shortest possible wires. Long, looping wires can introduce unwanted noise and interference into your circuit. They can also make it difficult to trace the connections. Cut your wires to the appropriate length and use wire strippers to remove the insulation. Pre-cut jumper wire kits are also a great option for keeping your wiring neat and tidy.
Third, always double-check your connections before applying power. This is the most important rule of breadboarding. A single misplaced wire can cause a short circuit and potentially damage your components. Take a few minutes to carefully review your circuit diagram and make sure that everything is connected correctly. It's much better to be safe than sorry. Also, remember to turn off the power before making any changes to your circuit.
Finally, don't be afraid to experiment. Breadboards are designed for experimentation. Try different components, different configurations, and different values. The best way to learn is by doing. And if you make a mistake, don't worry. That's part of the learning process. Just learn from your mistakes and keep on tinkering!
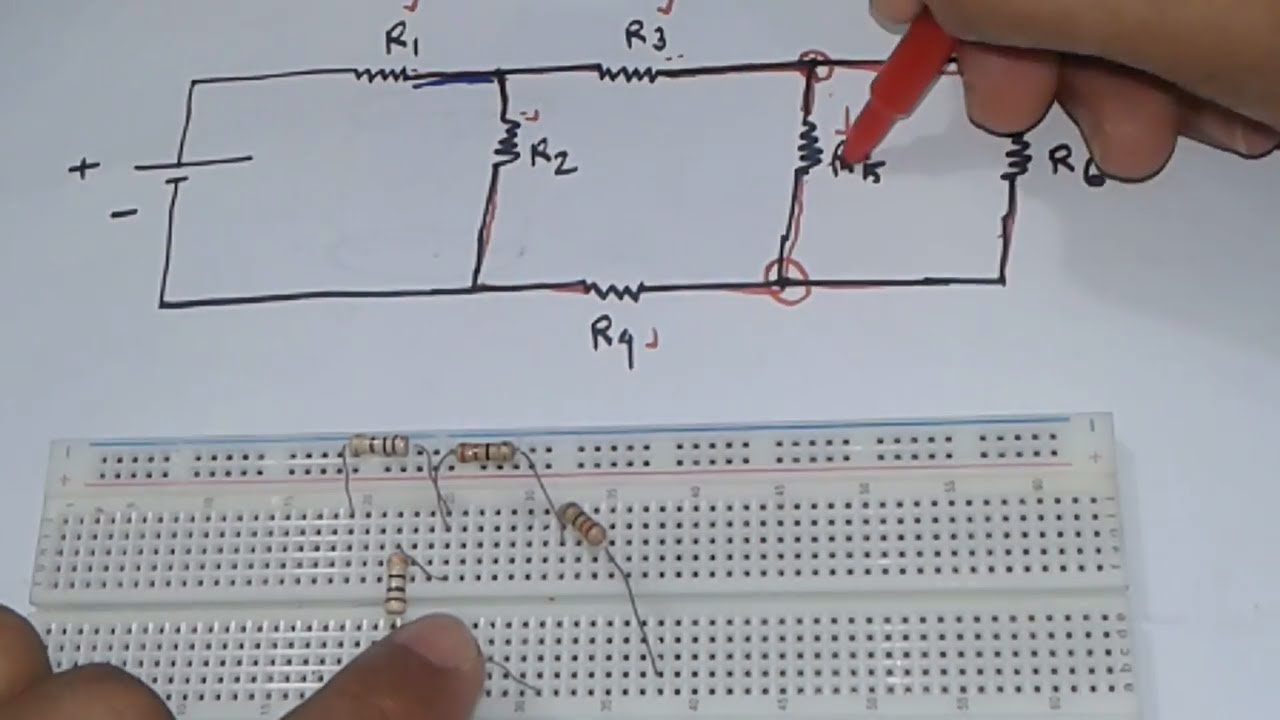
Circuit Diagram To Breadboard Examples
Troubleshooting Your Breadboard Creations
5. Debugging Like a Pro
Let's face it, building circuits isn't always smooth sailing. Sometimes things go wrong. The LED doesn't light up, the motor doesn't spin, or the smoke starts pouring out of your precious components (hopefully not!). But don't despair! Troubleshooting is an essential skill for any electronics enthusiast. And with a little patience and the right techniques, you can diagnose and fix most common circuit problems.
The first step in troubleshooting is to systematically check your connections. Are all the components properly inserted into the breadboard? Are the wires securely connected? Are there any loose connections or broken wires? Use a multimeter to check the continuity of your connections. A multimeter is an essential tool for any electronics hobbyist. It can be used to measure voltage, current, and resistance, which can help you identify problems in your circuit.
Next, check your power supply. Is it providing the correct voltage? Is it properly connected to the breadboard? Use your multimeter to measure the voltage at the power rails. Make sure that the polarity is correct (positive to positive, negative to negative). A reversed power supply can quickly damage your components.
If you've checked your connections and your power supply and the circuit still isn't working, it's time to start isolating the problem. Disconnect sections of the circuit one at a time to see if you can identify the culprit. For example, if you have a complex circuit with multiple stages, try disconnecting the last stage to see if that fixes the problem. If it does, then you know that the problem lies in the disconnected stage. And remember the mantra: simplify, simplify, simplify. Rebuild your circuit step-by-step from scratch.
And finally, when all else fails, don't be afraid to ask for help. There are many online forums and communities where you can get assistance with your electronics projects. Describe your problem in detail and provide as much information as possible about your circuit. A clear schematic diagram can be very helpful. And remember, there's no shame in asking for help. We all started somewhere, and we've all had our fair share of troubleshooting challenges.
